Traditional Chinese Medicine: A Beginner’s Guide to TCM
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is a holistic medical system that has been used for thousands of years to support balance, vitality, and long-term health. Rather than treating symptoms in isolation, TCM views the body as an interconnected whole, influenced by lifestyle, environment, emotional health, and internal energy.
This traditional Chinese medicine guide is designed to help you understand how TCM works, how it differs from Western medicine, and how practices like acupuncture, moxibustion, cupping, and Chinese herbal medicine are used to support the body’s natural healing processes.
Whether you are new to TCM or exploring integrative care, this guide offers a clear foundation.
TCM at a Glance:
Traditional Chinese Medicine focuses on restoring balance, not just managing symptoms
TCM views illness as a pattern of imbalance rather than a single diagnosis
Acupuncture, moxibustion, cupping, and Chinese herbs are personalized to each individual
Diagnosis in TCM relies on observation, pulse, tongue, and in-depth questions to discover the root causes
TCM is often used alongside Western medicine as part of a holistic, integrative approach
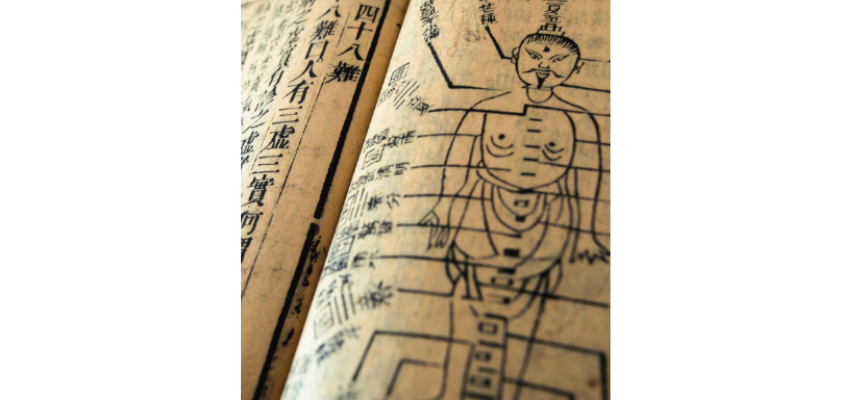
A Brief History of Traditional Chinese Medicine
Traditional Chinese Medicine has been practiced for thousands of years, with foundational texts dating back more than 2,000 years. These teachings evolved through generations of observation and clinical experience, long before modern diagnostic tools existed.
Unlike Western medicine, which focuses on anatomy, lab testing, and disease classification, TCM developed through an understanding of nature, seasonal rhythms, and the body’s response to its environment.
While Western medicine often addresses illness by targeting specific symptoms, TCM seeks to understand why imbalance developed in the first place. Today, many people use TCM alongside Western medicine to support both acute concerns and long-term wellness.
How Traditional Chinese Medicine Works
Yin and Yang Balance
In TCM, health is the result of balanced Yin and Yang. Yin represents cooling, nourishing, and restorative qualities, while Yang reflects warmth, movement, and activity. Illness occurs when these forces fall out of balance.
What Is Qi?
Qi (also spelled Chi) is the vital energy that powers all functions in the body, including digestion, circulation, and mental clarity. When Qi becomes stagnant, weak, or blocked, symptoms such as fatigue, headache, digestive discomfort, or chronic tension may arise.
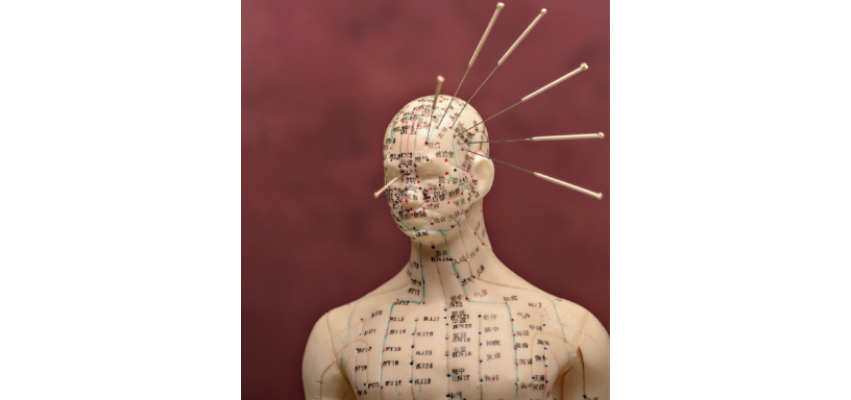
Meridians and Channels (Jing Luo)
Qi flows through pathways called meridians, or Jing Luo. These channels connect organs and systems throughout the body. TCM therapies stimulate specific points along these meridians to encourage balance and circulation.
Core Modalities Used in Traditional Chinese Medicine
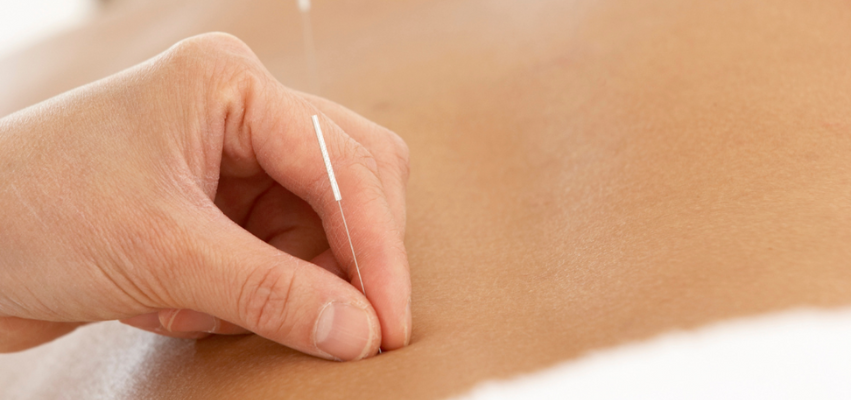
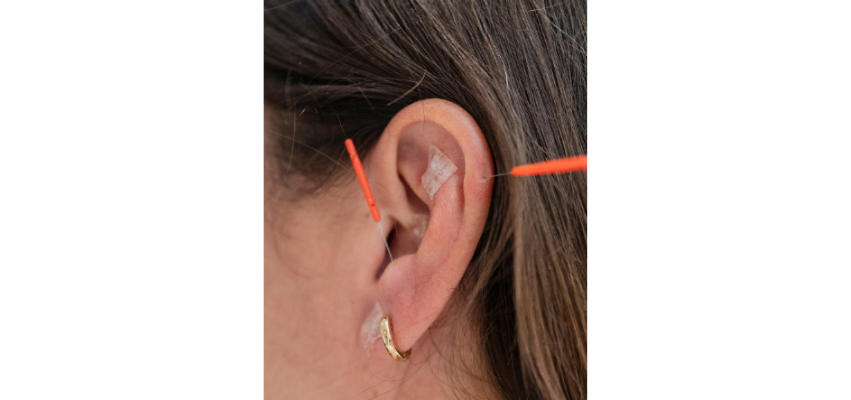
Acupuncture
Acupuncture uses very fine needles placed at specific points along the meridians to stimulate the nervous system, improve circulation, and support balance. It is commonly used for pain, stress, headaches, digestive concerns, and nervous system regulation.
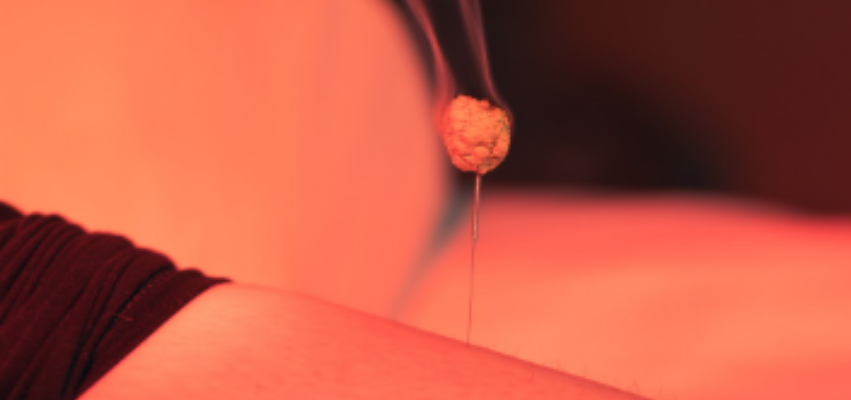
Moxibustion
Moxibustion involves the gentle warming of acupuncture points using mugwort. This technique is often used to support circulation, digestion, immune health, and cold or deficient patterns in the body.
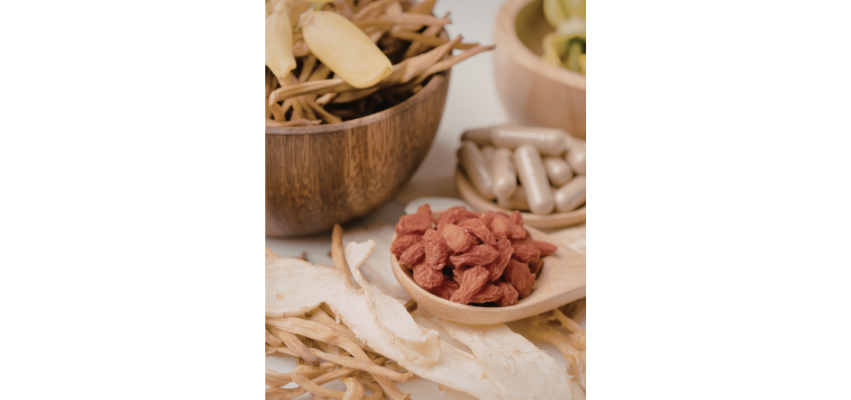
Chinese Herbal Medicine
Chinese herbal medicine uses carefully formulated combinations of herbs to address specific patterns of imbalance. These herbal medicines are highly personalized and may support digestion, stress resilience, hormonal balance, and overall vitality.
Cupping Therapy
Cupping uses suction cups placed on the skin to promote blood flow, release muscle tension, and move stagnant Qi. It is frequently used for muscle tightness, stress, and respiratory support.
Additional TCM Practices
Other practices used in TCM include dietary therapy, lifestyle guidance, gua sha, and gentle movement practices like tai chi, all aimed at supporting balance and prevention.
The 8 Principles of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Ba Gang)
The Ba Gang system helps TCM practitioners understand patterns of imbalance using eight guiding principles, including internal vs external, hot vs cold, excess vs deficiency, and yin vs yang.
TCM Organ Systems
TCM organs represent functional systems rather than anatomical structures alone.
The Zang organs (Heart, Liver, Spleen, Lung, Kidney) store vital substances such as Qi and blood.
The Fu organs (Stomach, Small Intestine, Large Intestine, Gallbladder, Bladder) focus on digestion, absorption, and elimination.
Each organ system is linked to emotional health, energy flow, and physical function.
How Illness Is Diagnosed in Traditional Chinese Medicine
TCM diagnosis looks at the whole person rather than isolated symptoms:
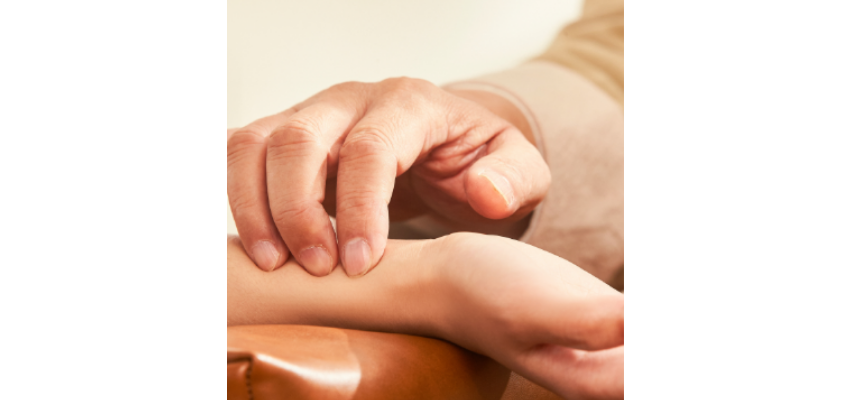
Pulse Diagnosis — the pulse is assessed at multiple positions and depths to evaluate organ function and Qi quality.
Tongue Diagnosis — the tongue provides insight into digestion, circulation, and internal balance through its color, shape, and coating.
Observation and Questioning — detailed questions about sleep, digestion, stress, and energy help identify patterns contributing to illness.
Benefits of Traditional Chinese Medicine
A holistic, whole-body approach to health
Emphasis on prevention and long-term balance
Highly personalized treatment plans
Support for both physical and emotional wellbeing
Integrative care that complements Western medicine
What Modern Research Is Showing
Research continues to explore the health benefits of traditional Chinese medicine. Studies suggest acupuncture may help stimulate the nervous system, improve circulation, and reduce inflammation. Chinese herbal medicine shows potential benefits for digestive health, immune function, and stress response.
While TCM does not replace Western medicine, it is increasingly used as a complementary, integrative approach to care.
What to Expect When Visiting a TCM Practitioner
A first visit typically includes a comprehensive intake, pulse and tongue assessment, and a personalized treatment plan. Sessions are unhurried and focused on understanding root causes rather than quick fixes.
At Calm Spirit, TCM-inspired services such as acupuncture, moxibustion, cupping, and herbal support are thoughtfully integrated to support both immediate concerns and long-term wellness. You can explore our range of services here.
Exploring Traditional Chinese Medicine at Calm Spirit
Traditional Chinese Medicine offers a grounded, time-tested approach to health that emphasizes balance, prevention, and individualized care. Whether you are navigating a specific concern or looking to support your overall wellbeing, TCM provides tools that work with the body rather than against it.
If you are curious about acupuncture, moxibustion, cupping, or Chinese herbal support, our team at Calm Spirit is here to guide you with care, education, and an integrative perspective.
You can schedule an appointment or free consultation here, connect with us on our contact page, or give us a call at 303-467-5337.